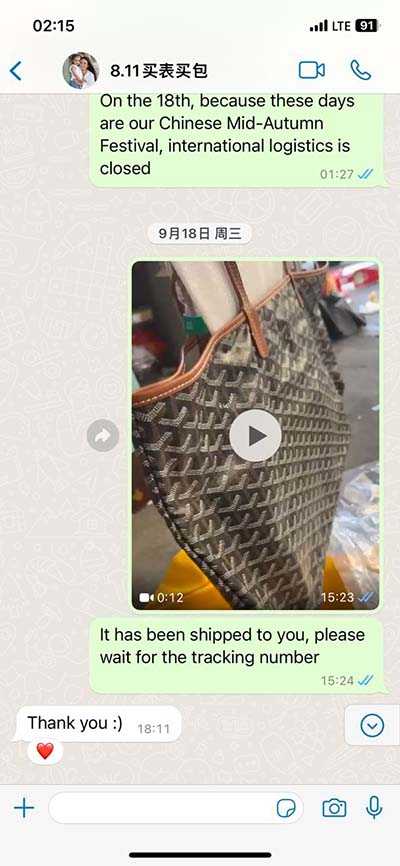
why do liberals watch fake news | Truth and Bias, Left and Right: Testing Ideological Asymmetries why do liberals watch fake news As for where the market for liberal fake news comes from, according to Claire Wardle, who is a research director at First Draft - a non-profit organisation which is looking for solutions. The new DELFI Android app has been completely redesigned with a fresh look and feel to give you the best experience. It gives you everything you've come to expect and love from the Latvian.
0 · You are fake news: political bias in perceptions of fake news
1 · Why Our Brains Love Fake News—and How We Can Resist It
2 · Truth and Bias, Left and Right: Testing Ideological Asymmetries
3 · The rise of left
4 · The relationship between political affiliation and beliefs about
5 · The Real Impact of Fake News: The Rise of Political
6 · Media bias against conservatives is real, and part of the
7 · Fake news is fooling more conservatives than liberals. Why?
8 · Fake News, Big Lies: How Did We Get Here and Where Are We
9 · Democrats vs. Republicans: Who spots fake news more?
DELFI - Latvijas populārākais ziņu portāls. Aktuālās ziņas katru dienu, kā arī daudz citu jaunumu un izklaides - lasi DELFI.
As for where the market for liberal fake news comes from, according to Claire Wardle, who is a research director at First Draft - a non-profit organisation which is looking for solutions.
The debate around “fake news” has raised the question of whether liberals and conservatives differ, first, in their ability to discern true from false information, and second, in their tendency to give more credit to information that is ideologically congruent. Conservatives overwhelmingly associate the liberal media outlet ‘CNN’ with ‘fake news’ (75%), whereas liberals identify the conservative outlet ‘Fox’ as ‘fake news’ (59%). Importantly, it is primarily conservatives who think of the mainstream media as . The Real Impact of Fake News: The Rise of Political Misinformation—and How We Can Combat Its Influence. Political Analytics. Strategic Communication. What is the difference between misinformation and disinformation? Van Bavel explained to NYU News the downsides to our deeply human desire for belonging, and offered some possible tactics for fostering evidence-based thinking. Here are some of his thoughts on how better understanding the brain could help encourage more productive political conversations.
This idea that the media is made up of unselfconsciously liberal elites who don't even recognize the biases they have against conservative policies and conservatives in general goes back decades,.
You are fake news: political bias in perceptions of fake news
Why Our Brains Love Fake News—and How We Can Resist It
President Joe Biden asked the country on the first anniversary of the January 6 insurrection at the U.S. Capitol. But distinguishing truth from lies can be a difficult task when every day Americans read and hear false “facts”—misinformation—and deliberately misleading information created to cause harm—disinformation. The rise of the phrase “fake news” as an alternative label for what might at times be considered propaganda is politically and psychologically intriguing, and leads to interesting questions: Which news sources do people consider real news, or fake news, and why? Do the news sources people categorize as fake news differ from those they . Structural shifts may explain why conservative voters seem to be more prone to the infodemic, and why conservative leaders have more reason—and are more likely—to undermine reliable sources.01/22/2024. Democrats have a higher success rate than Republicans in spotting fake news, a recent study has suggested. It also shows education level and gender play a crucial role in the.
As for where the market for liberal fake news comes from, according to Claire Wardle, who is a research director at First Draft - a non-profit organisation which is looking for solutions. The debate around “fake news” has raised the question of whether liberals and conservatives differ, first, in their ability to discern true from false information, and second, in their tendency to give more credit to information that is ideologically congruent. Conservatives overwhelmingly associate the liberal media outlet ‘CNN’ with ‘fake news’ (75%), whereas liberals identify the conservative outlet ‘Fox’ as ‘fake news’ (59%). Importantly, it is primarily conservatives who think of the mainstream media as .

The Real Impact of Fake News: The Rise of Political Misinformation—and How We Can Combat Its Influence. Political Analytics. Strategic Communication. What is the difference between misinformation and disinformation? Van Bavel explained to NYU News the downsides to our deeply human desire for belonging, and offered some possible tactics for fostering evidence-based thinking. Here are some of his thoughts on how better understanding the brain could help encourage more productive political conversations.
Truth and Bias, Left and Right: Testing Ideological Asymmetries
This idea that the media is made up of unselfconsciously liberal elites who don't even recognize the biases they have against conservative policies and conservatives in general goes back decades,. President Joe Biden asked the country on the first anniversary of the January 6 insurrection at the U.S. Capitol. But distinguishing truth from lies can be a difficult task when every day Americans read and hear false “facts”—misinformation—and deliberately misleading information created to cause harm—disinformation.
The rise of the phrase “fake news” as an alternative label for what might at times be considered propaganda is politically and psychologically intriguing, and leads to interesting questions: Which news sources do people consider real news, or fake news, and why? Do the news sources people categorize as fake news differ from those they . Structural shifts may explain why conservative voters seem to be more prone to the infodemic, and why conservative leaders have more reason—and are more likely—to undermine reliable sources.01/22/2024. Democrats have a higher success rate than Republicans in spotting fake news, a recent study has suggested. It also shows education level and gender play a crucial role in the. As for where the market for liberal fake news comes from, according to Claire Wardle, who is a research director at First Draft - a non-profit organisation which is looking for solutions.
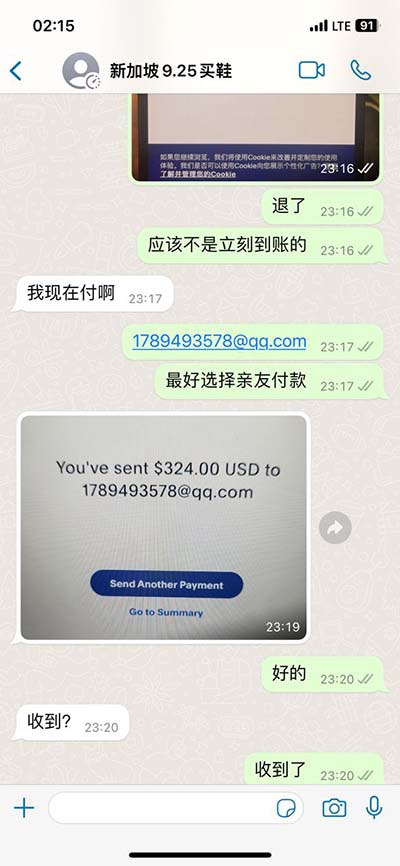
gucci wallet and money clip
The debate around “fake news” has raised the question of whether liberals and conservatives differ, first, in their ability to discern true from false information, and second, in their tendency to give more credit to information that is ideologically congruent. Conservatives overwhelmingly associate the liberal media outlet ‘CNN’ with ‘fake news’ (75%), whereas liberals identify the conservative outlet ‘Fox’ as ‘fake news’ (59%). Importantly, it is primarily conservatives who think of the mainstream media as . The Real Impact of Fake News: The Rise of Political Misinformation—and How We Can Combat Its Influence. Political Analytics. Strategic Communication. What is the difference between misinformation and disinformation? Van Bavel explained to NYU News the downsides to our deeply human desire for belonging, and offered some possible tactics for fostering evidence-based thinking. Here are some of his thoughts on how better understanding the brain could help encourage more productive political conversations.
This idea that the media is made up of unselfconsciously liberal elites who don't even recognize the biases they have against conservative policies and conservatives in general goes back decades,. President Joe Biden asked the country on the first anniversary of the January 6 insurrection at the U.S. Capitol. But distinguishing truth from lies can be a difficult task when every day Americans read and hear false “facts”—misinformation—and deliberately misleading information created to cause harm—disinformation. The rise of the phrase “fake news” as an alternative label for what might at times be considered propaganda is politically and psychologically intriguing, and leads to interesting questions: Which news sources do people consider real news, or fake news, and why? Do the news sources people categorize as fake news differ from those they .
Structural shifts may explain why conservative voters seem to be more prone to the infodemic, and why conservative leaders have more reason—and are more likely—to undermine reliable sources.

The rise of left
Atsauksmes par veikalu Deltamobile.lv. Esi pirmais, kurš novērtē interneta veikalu Deltamobile.lv! Jūsu atsauksme par veikalu Deltamobile.lv. Jūsu vērtējums veikalam Deltamobile.lv 5 4 3 2 1 . Vārds, Uzvārds * E-pasts * Pasūtījuma numurs; Atsauksme * (Max 1000 simboli) Pievienot atsauksmi
why do liberals watch fake news|Truth and Bias, Left and Right: Testing Ideological Asymmetries